styled-component+ts props 전달하기
typescript환경에서 styled-components에 props를 전달하려면 제네릭을 활용하면 된다.
나는 next.js를 사용중이라 @emotion/styled를 사용하였다.
예시
1 | interface blockType { |
실제 사용할 때는 컴포넌트에 props를 내려주고 접근하여 사용하면 된다.
1 | <BlockWrapper> |
typescript환경에서 styled-components에 props를 전달하려면 제네릭을 활용하면 된다.
나는 next.js를 사용중이라 @emotion/styled를 사용하였다.
1 | interface blockType { |
실제 사용할 때는 컴포넌트에 props를 내려주고 접근하여 사용하면 된다.
1 | <BlockWrapper> |
axios는 요청을 취소할 수 있는 CancelToken을 제공한다.
1 | cancelToken = axios.CancelToken.source(); |
토큰을 생성하여 axios의 config에 넣어주면 된다.
그 후 토큰의 cancel()메서드를 호출하면 된다.
아래의 코드는 리액트에서 사용한다고 가정하고 예시로 작성해본 코드이다..!
1 | const Example = () => { |
마지막 요청만 서버로 보내는 디바운싱과 함께 적용하면 요청을 효율적으로 관리할 수 있을 것 같다.
디바운싱을 적용하여 간단하게 작성해보았다.
1 | const Example = () => { |
다음에 진행할 프로젝트에 꼭 한 번 적용해보고 싶다!
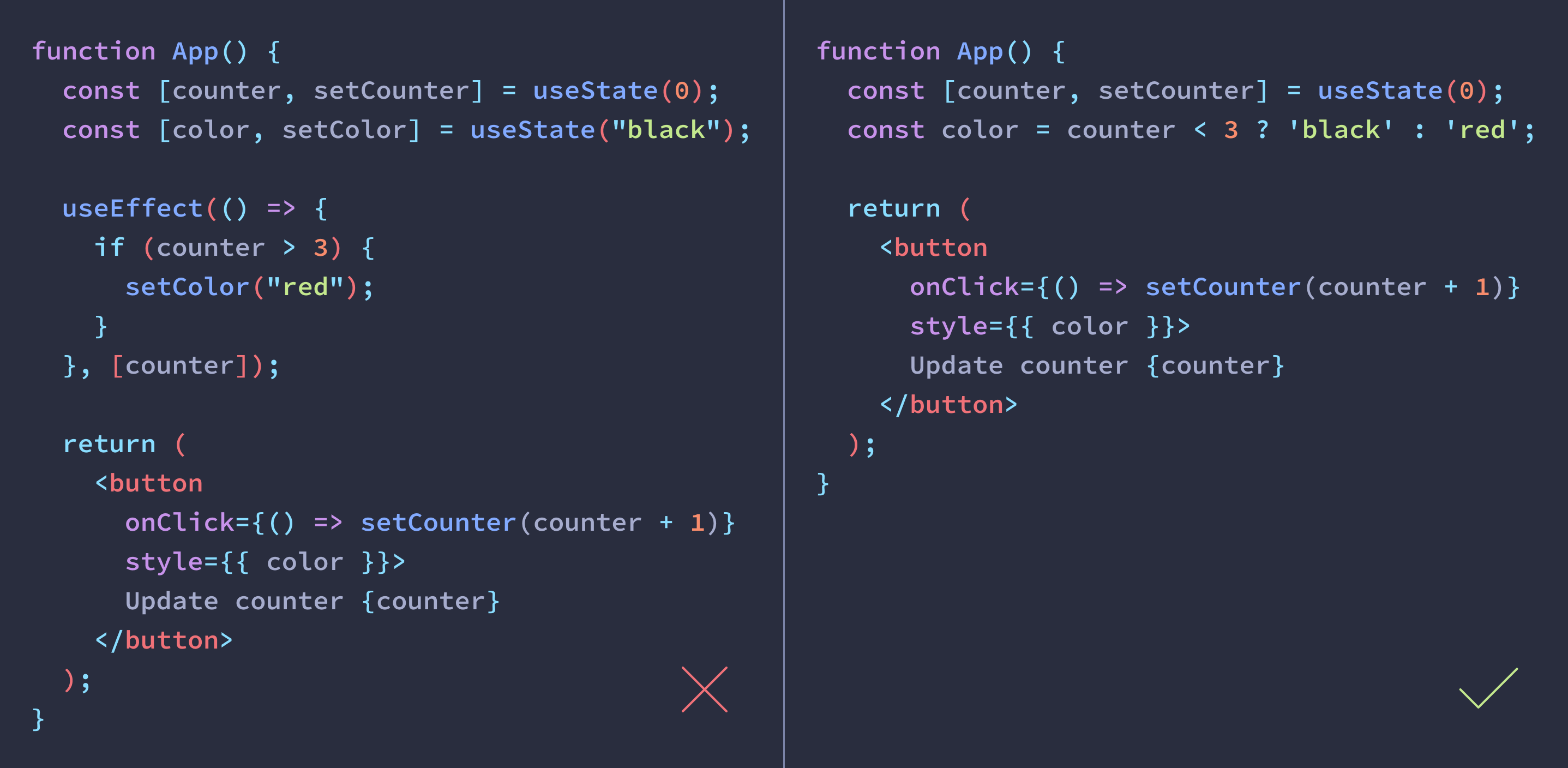
count에 따라 색을 다르게 하는 코드이다.
왼쪽 코드는 counter가 증가할 때마다 useEffect에서 color의 변화가 일어난다.
즉 렌더링이 두 번 일어난다.
그에 비해 오른쪽 코드는 counter가 변화할 떄마다 counter에 따라 color를 다르게 한다.
즉 한 번의 렌더링으로 같은 기능을 한다.
state를 새로 만들기 전에 기존 state로 처리할 수 있는지 생각하고 만들자!
https://twitter.com/asidorenko_/status/1483473130383450114?s=20
지금까지 setState의 두 번째 파라메터로 콜백함수를 넣어 동기실행을 할 수 있다고 알고 있었는데
이는 클래스형 컴포넌트의 setState에만 존재한다.
즉 다음과 같은 실행은 불가능하다.
1 | const [state, setState] = useState(0); |
하지만 useEffect를 사용하여 다음과 같은 방법으로 대체할 수 있다.
useEffect의 의존성 배열에 state를 추가하여 실행하는 방법이다.
1 | const [state, setState] = useState(0); |
antd+typescript+react를 사용하던 중 ref의 세 가지 타입에 대해 알게되어 포스팅한다.
react의 useRef는 세 가지 타입이 오버로딩 되어있다.
useRef는 initialValue를 useRef 객체의 current에 저장한다.
이 useRef의 current가 변경되어도 컴포넌트는 리렌더링 되지 않는다.
때문에 DOM 내부 객체를 직접 가리키거나 렌더링과 상관없는 변수를 저장하는데에 사용된다.
MutableRefObject<T>1 | function useRef<T>(initialValue: T): MutableRefObject<T>; |
initialValue의 타입과 제네릭의 타입이 T인경우 MutableRefObject<T>를 반환한다.
렌더링과 관련없는 값을 저장하는데에 사용하자.
RefObject<T>1 | function useRef<T>(initialValue: T | null): RefObject<T>; |
제네릭의 타입이 T이고 initialValue의 타입이 T 혹은 null인 경우 RefObject<T>를 반환한다.RefObject<T>는 readonly로 current를 직접 수정할 수 없다.
하지만 current의 하위 프로퍼티는 조작 가능하다.
그렇기에 DOM 을 조작하기 위해 사용하자.
MutableRefObject<T|undefined>1 | function useRef<T = undefined>(): MutableRefObject<T | undefined>; |
ts+react를 사용할 때에 HTMLEvent의 타입을 지정하는 방법에 대해서 간단하게 정리해보았다.
Event의 타입은 React안에 정의되어있다.
onchange 이벤트의 타입은 React.ChangeEvent<T>이다.onclick 이벤트의 경우 React.MouseEvent<T>이다.
제네릭에는 이벤트를 발생시키는 요소를 전달하면 된다.
자주 쓰이는 useInput hooks이다.
이벤트의 타입을 React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>라고 명시해주었다.
1 | import React, { useState, useCallback } from "react"; |
다음 플러그인 사용하기
https://www.npmjs.com/package/next-compose-plugins
1 | const withTM = require("next-transpile-modules")([ |
next.js의 경우 node_modules내부의 패키지에서 전역으로 css를 import하면 에러를 발생시킨다.
구글링을 통해 해결하였다.
1 | ./node_modules/@fullcalendar/common/main.css Global CSS cannot be imported from within node_modules. Read more: https://err.sh/next.js/css-npm Location: node_modules/@fullcalendar/common/main.js |
1 | npm i next-transpile-modules @babel/preset-react |
next-transpile-modules 는 node_modules 내부의 패키지에 css/scss파일이 포함 될 수 있도록 transpile 하는 플러그인이다.
이후 next.config.js 파일을 다음과같이 작성해주었다.
1 | /** @type {import('next').NextConfig} */ |
공부할 예정인 next-compose-plugins를 통해 간편하게 여러 플러그인을 import 할 수 있다.
next css-npm
How To Use Fullcalendar With Next.js (v10 or higher)
render() 함수는 다음 중 하나를 반환하여야한다.
render()를 통하여 여러개의 Element를 반환한다.render()는 순수한 함수여야 한다.
컴포넌트의 state를 변경하지 않고 호출될 때마다 동일한 결과를 반환해야한다.
또한 브라우저와 직접적으로 상호작용해서는 안된다.
ReactNode는 ReactChild 등등 많은 것을 포함한다.
제일 범용적으로 사용할 수 있는 것 같다..!(다른 관점에선 리펙토링 할 수 있는 부분)
클래스형 컴포넌트의 반환값이다!
1 | type ReactNode = |
ReactElement는 type, props, 그리고 key를 가진 객체이다.
예전 게시글에서 알아본 것 처럼 함수형 컴포넌트의 반환값이다!
1 | interface ReactElement< |
JSX.Element는 any type의 generic type인 ReactElement이다.
전역으로 선언되어있어 라이브러리들이 구현하여 사용할 수 있다.
1 | declare global { namespace JSX { interface Element extends React.ReactElement<any, any> { } |
React.FC는 children이 포함되어있어 컴포넌트의 props의 타입 처리가 어렵다.
차라리 위의 ReactElement나 ReactNode를 적용 후 children의 타입을 명시하는 것이 좋다..!
next를 사용하던 도중 SSR(Server Side Rendering)에서 사용되는 hydrate라는 키워드에 대해 공부하고 싶어져서 공부해보았다.
react-dom은 앱의 최상위 레벨에서 사용하는 DOM과 관련한 메서드와 React 모델 외부로 나갈 수 있는 해결책을 제공한다.
cra로 만든 프로젝트 기준 최상위 레벨인 index.js에서 사용된다.
render 메소드를 제공해주는 그 패키지이다.
1 | import React from "react"; |
1 | ReactDOM.render(element:React$Element<any>,container:Container,callback:?Function,) |
render는 element를 container DOM에 렌더링하고 컴포넌트에 대한 참조(Ref)를 반환한다.
callback이 제공되면 렌더링되거나 업데이트 된 후에 실행된다.
element가 이전에 container내부에 렌더링 되었다면 해당 엘리먼트는 업데이트하고 최신의 React 엘리먼트를 반영하는 데 필요한 DOM만 변경한다.
일전에 공부하였던 diff 알고리즘과 React fiber를 통하여 DOM에 변경점만 업데이트 하거나 렌더링하는 함수이다.
ReactDOM에서 render 함수를 볼 수 있다.
동작방식은 다음과 같다.
container가 DOM 엘리먼트인지 확인하고 아닐경우 에러를 발생시킨다.
root 엘리먼트는 _reactRootContainer 속성을 가지고 있다.
또한 container는 __reactContainere+$랜덤 문자열 속성도 가지고 있다.
다음 경우 에러를 발생시킨다.
container의 __reactRootContainer 속성이 undefined일 경우container 내부에 __reactContainerer+$랜덤 문자열 속성이 존재하지 않을 경우2까지 에러가 발생하지 않았을 경우 DOM 엘리먼트인 container의 sub tree로 React 엘리먼트인 element를 render한다.
1 | export function render( |
공식문서에 나와있는 주의사항은 다음과 같다.
ReactDOM.render()는 처음 호출할 때 기존의 DOM 엘리먼트를 교체하며 이후의 호출은 React의 DOM diffing 알고리즘을 사용하여 더욱 효율적으로 업데이트한다.
ReactDOM.render()는 컨테이너 노드를 수정하지 않고 컨테이너의 하위 노드만 수정하여 자식 노드를 덮어쓸 필요 없이 기존의 DOM 노드에 컴포넌트를 추가할 수 있다.
ReactDOM.render()는 현재 ReactComponent 루트(root) 인스턴스에 대한 참조를 반환한다. 그러나 이 반환 값을 사용하는 것은 피해야한다.
ReactComponent 인스턴스의 참조가 필요하다면 권장하는 해결책은 루트 엘리먼트에 콜백 ref를 붙여야한다.
ReactDOM.render()를 사용해 서버에서 렌더링한 컨테이너에 이벤트를 보충할 때는 hydrate()를 사용해야 한다.
1 | ReactDOM.hydrate(element:React$Element<any>,container:Container,callback:?Function,) |
위의 render와 동일하지만 HTML이 ReactDOMServer로 렌더링 된 후 컨테이너에 이벤트를 보충하기 위해 사용된다.
React는 기존 마크업에 이벤트 리스너를 연결한다.
서버에서 온 정적인 HTML코드에 React 코드들을 렌더링하여 리액트가 관리할 수 있도록 컴포넌트화 하는 함수이다.
SSR을 하는 경우에는 hydrate로 콜백만 붙여야 한다.(고한다.)
마찬가지로 ReactDOM에서 hydrate 코드를 볼 수 있다.
render와 동작 방식이 똑같다.
다만 render와 달리legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer 함수에서 forceHydrate가 true이다.
1 | return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer( |
1 | export function hydrate( |